The Whole Story of How Humans Evolved From Great Apes
The Whole Story of How Humans Evolved From Great Apes
Humans and great apes, such as chimpanzees, bonobos, gorillas, and orangutans, share a common ancestor that lived approximately 6-8…
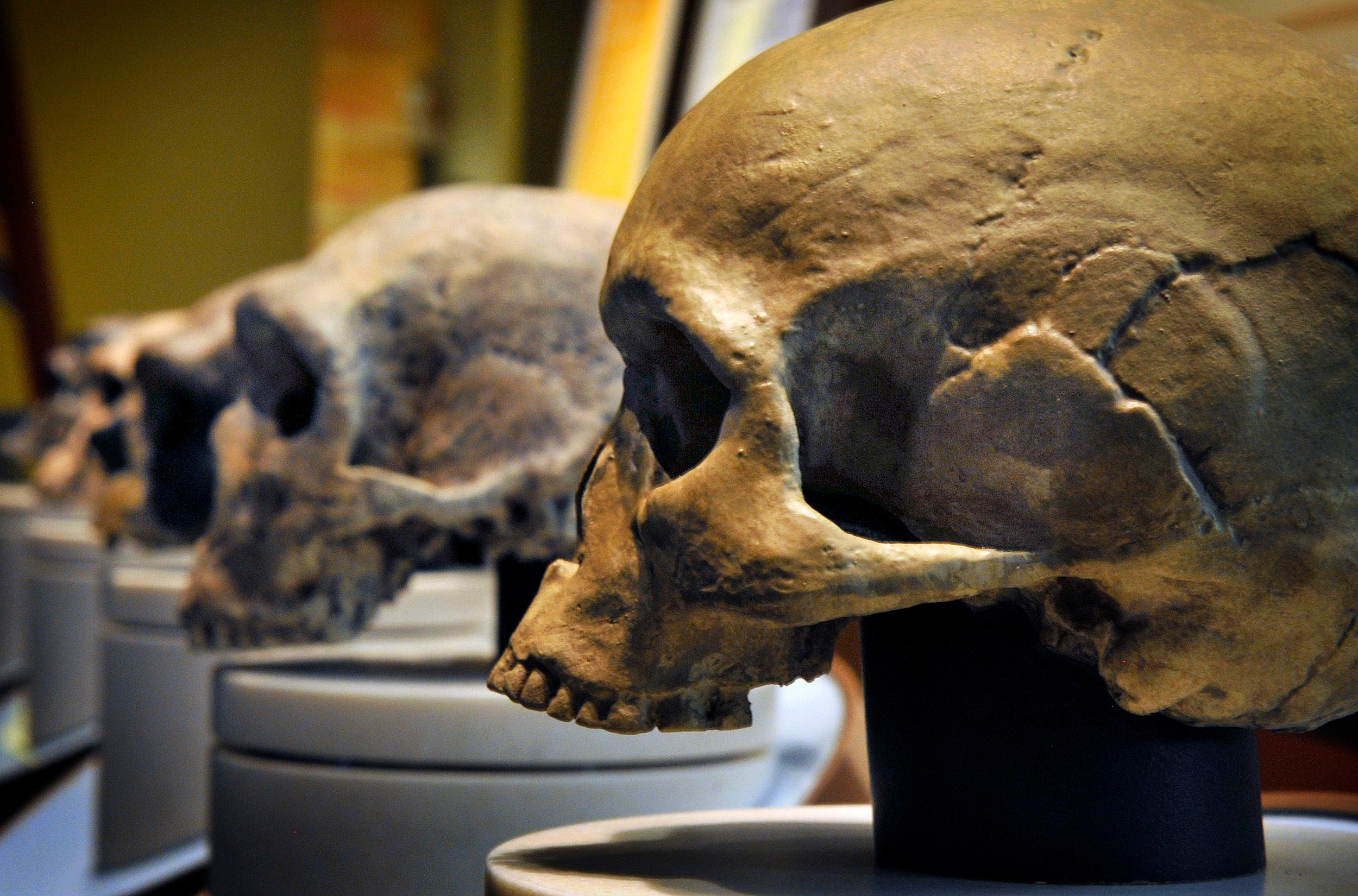

The Whole Story of How Humans Evolved From Great Apes
Humans and great apes, such as chimpanzees, bonobos, gorillas, and orangutans, share a common ancestor that lived approximately 6-8 million years ago.
Over time, this common ancestor diverged into separate evolutionary paths, with one leading to modern humans and the other to modern great apes.
One of the key factors in human evolution was the development of bipedalism, or walking on two legs, which freed up our hands for tool use and other activities.
Another important aspect of human evolution was the expansion of our brains, particularly the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as decision-making and problem-solving.
Throughout our evolutionary history, humans have adapted to their environments through changes in diet, behavior, and social structures.
The discovery of fire and the development of language were also critical milestones in human evolution, enabling us to cook food, communicate complex ideas, and collaborate on tasks.
Modern humans, or Homo sapiens, are the only surviving species of the genus Homo, which includes other extinct species such as Homo neanderthalensis and Homo habilis.
Despite these evolutionary differences, humans share over 98% of their DNA with great apes, highlighting our close genetic relationship.
Overall, the story of how humans evolved from great apes is a fascinating tale of adaptation, innovation, and survival that continues to shape our understanding of ourselves and our place in the natural world.